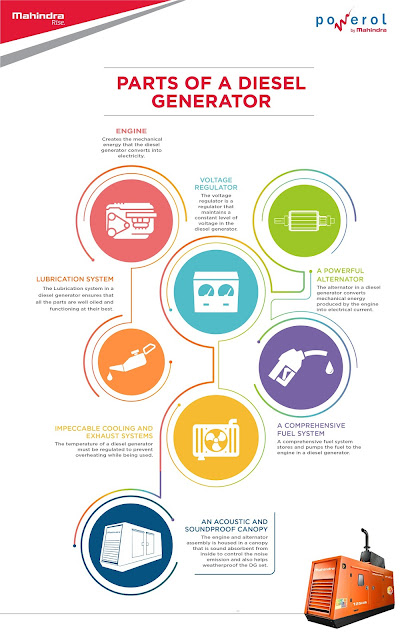
Parts of a diesel generator and their functions.
We all know that a diesel generator
is used as a source of backup when supply of power is not constant. They have assumed
great importance and have almost become a necessity for households and
companies in areas where there is a shortage of electrical supply. Given the
promising nature of a diesel generator, we all have at some point used it or at
least have known its merits. But have we ever tried to understand what are the
various parts that power the diesel generator and help it function?
Let us look at some of the main
components of a diesel generator and their functions:
1.
Engine – The heart of the system
The function of the engine is to
create the mechanical energy that the diesel generator converts into
electricity. The design of the engine is aimed at generating a maximum supply
of electrical current by running on diesel or other alternate fuels.
2.
A comprehensive fuel system
Generators that run on
diesel or any other fuel, have a fuel system that stores and pumps it to the
engine. The tank stores a good amount of fuel to power the generator for several hours at a stretch. A fuel pipe in the system connects the tank to the engine while a
return pipe connects the engine to the fuel tank for the return of fuel. A fuel
pump moves fuel from the tank through fuel pipe and to the engine. There is a
fuel filter which filters out debris from the fuel, if any before delivering it
to the engine. A fuel injector atomizes and injects the fuel directly into the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The alternator in a diesel generator
converts mechanical energy produced by the engine into electrical current. It
comprises of the stator and the rotor (or armature). The stator is stationary and
contains a set of coils that conduct electricity. The rotor moves to create a
constantly rotating electromagnetic field around the stator.
4.
Voltage Regulator
The alternator may generate
electrical voltage but the level of voltage needs to be
regulated that is suitable for practical use. Voltage regulator is an
electrical regulator that maintains a constant level of voltage.
5.
Impeccable cooling and exhaust systems
The temperature of a diesel generator must
be regulated to prevent overheating while being used. Generators can use a fan,
coolant or both to control the temperature of the generator at work. The
internal combustion engines are usually cooled by passing engine coolant
through the engine block. The generator also produces exhaust as the combustion
chamber converts fuel. There are exhaust systems that dispel harmful gases
emitted.
6.
Lubrication system
A diesel generator comprises of
various moving parts. These parts need to be oiled for their smooth
functioning. The lubrication system ensures that the parts are well oiled and
functioning at their best.
7.
Acoustic Enclosure
Being a mechanical product with
many moving parts, a diesel engine makes lot of noise during its operation. In
order to control the noise emission, the engine and alternator assembly is
housed in a soundproof canopy having sound absorbent material from inside. As
per Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), the maximum noise emission from a
generator should not exceed 75 dBA from 1 m distance from the canopy.
For more information about diesel
generators, please visit: http://www.mahindrapowerol.com/ or
call us at Toll Free: - 1-800-419-1999